HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. It is a complete home comfort system that regulates indoor temperature and air quality. While often confused with the term AC (air conditioning), HVAC encompasses a broader range of functions, including heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
Understanding how your HVAC works is essential for several reasons. First, it allows you to properly maintain your system, providing optimal performance and a longer lifespan. A well-maintained HVAC system operates more efficiently, saving you money on energy bills and reducing your carbon footprint.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of HVAC systems. We’ll explore the different components that make up an HVAC system, how they work together to heat and cool your home, and the various types of systems available, such as split systems, ductless systems, and heat pumps.
Contents
- 1 What Is An HVAC System And What Does HVAC Stand For?
- 2 How Does HVAC System Work?
- 3 Types of HVAC Systems
- 4 Components of HVAC Systems
- 5 How to Choose the Right HVAC Brand?
- 6 Importance of HVAC Systems
- 7 How to Choose an HVAC Company for Installation and Maintenance
- 8 Contact HVAC Angel For All Your HVAC Needs
- 9 Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An HVAC System And What Does HVAC Stand For?
An HVAC system is a comprehensive solution designed to regulate indoor environments by providing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
At the core of an HVAC system are the heating and cooling units. The heating component, such as a furnace or heat pump, warms the air during colder months, while the air conditioning unit or cooling system removes heat and humidity from the air during warmer seasons. These units work in tandem with the ventilation system, which includes a network of ducts and vents that circulate the conditioned air throughout your home.
The ventilation aspect of an HVAC system helps in maintaining indoor air quality. By continuously circulating air, the system helps remove contaminants, odors, and excess moisture, creating a healthier living environment.
An HVAC system is an integral part of modern living, providing the ability to control your indoor environment regardless of the weather outside. By regulating temperature, humidity, and air quality, an HVAC system contributes to the overall comfort, health, and well-being of you and your family.
How Does HVAC System Work?
Operation of Heating Systems
The heating system relies on a fuel or energy source, such as natural gas, oil, or electricity, to generate heat. Depending on the type of system, this heat is produced by either a furnace or a boiler.
Furnaces are the most common type of heating system in HVAC. They burn fuel or use electrical resistance to generate heat, which is then distributed throughout your home via a network of ducts. As the furnace heats the air, the air handler draws in the cold air, filters it, and pushes the warmed air through the ducts and out of the vents in each room.
Boilers, on the other hand, heat water to produce steam or hot water, which is then circulated through a system of pipes to radiators or baseboard heaters in each room. This radiant heat warms the air in the room, providing a consistent and comfortable temperature.
The thermostat is the control center of your HVAC system’s heating operation. When the temperature in your home drops below the desired setpoint, the thermostat signals the heating system to turn on and begin the heating cycle. Once the desired temperature is reached, the thermostat signals the system to turn off, maintaining a comfortable environment while conserving energy.
Operation of Ventilation Systems
The ventilation system works by circulating air throughout your home. Air circulation is achieved through the use of fans and blowers within the HVAC system. These components work to move air through the ductwork, so that conditioned air reaches every room in your home. As the air circulates, it passes through an air filter, which traps dust, pollen, and other particles, helping to improve indoor air quality.
Humidity control is another essential aspect of ventilation. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), indoor humidity levels above 60% can promote mold growth and increase allergen levels, negatively impacting air quality indoors.
To combat this, HVAC systems may include humidifiers to add moisture during dry months and dehumidifiers to remove excess moisture during humid seasons, maintaining optimal humidity levels for your health and comfort.
Operation of Air Conditioning Systems
Air conditioning systems, a key component of HVAC, work by using the refrigeration cycle to remove heat from indoor air and release it outdoors. This process involves several steps, including evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion.
The refrigeration cycle begins with the refrigerant entering the indoor evaporator coil. As warm air from your home passes over the coil, the refrigerant evaporates, absorbing heat from the air and cooling it down. The cooled air is then distributed throughout your home via the ductwork, with the help of the blower fan.
Next, the refrigerant, now in a gaseous state, moves to the compressor, where it is compressed, increasing its temperature and pressure. The high-temperature, high-pressure refrigerant gas then flows to the outdoor unit, which contains the condenser coil.
As the hot refrigerant gas passes through the condenser coil, it releases its heat to the outside air, causing the refrigerant to condense back into a liquid state. A fan in the outdoor unit helps to facilitate this heat transfer by blowing air across the condenser coil.
Finally, the cooled liquid refrigerant passes through an expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and cools it further before it returns to the indoor evaporator coil to begin the cycle again.
Throughout this process, the thermostat acts as the control center for the air conditioning system. When the indoor temperature rises above the desired setpoint, the thermostat signals the AC unit to start the cooling cycle. Once the desired temperature is reached, the thermostat signals the system to turn off, conserving energy while maintaining a comfortable environment.
Types of HVAC Systems
Air Conditioning Systems
When it comes to ac, there are several types of systems available, each with its own unique features and benefits. Understanding the differences between these systems can help you choose the best option for your home.
1. Central AC Systems
Central air conditioners consist of an indoor unit and an outdoor unit, which houses the compressor. These systems are powerful, efficient, and can cool your entire home. However, they require ductwork, which can be expensive to install if your home doesn’t already have it.
2. Ductless Mini-Splits
Ductless mini-split systems have an outdoor condenser and one or more indoor units. They don’t require ductwork, making them a great option for older homes or additions. Each indoor unit can be controlled separately, allowing you to cool specific rooms or zones.
3. Ductless Multi-Split Systems
Similar to ductless mini-splits, multi-split systems use a single outdoor compressor connected to multiple indoor units. This allows you to cool or heat multiple rooms or even your entire home, while still maintaining the ability to control the temperature in each zone separately.
4. Ducted Mini-Split Systems
Ducted mini-split systems use smaller tubes instead of traditional large ducts to distribute conditioned air throughout your home. They are a good choice for homes with limited space for conventional ductwork and offer better air circulation compared to ductless mini-split systems.
5. Other Air Conditioners
Window units and portable air conditioners are less expensive options that can cool a single room at a time. Window units combine the air handler and condenser in one unit. Portable air conditioners connect to a window via removable tubing and can be stored during cooler months.
Heating Systems
When it comes to heating your home, there are several types of systems available, each with its own unique features and benefits.
1. Boilers
Boilers heat water to produce steam, which is then distributed through a network of radiators to heat your home. They do not use forced air and can run on various fuels such as natural gas, propane, heating oil, electricity, or wood. While less common in homes, boilers provide a gentle, radiant heat that some homeowners prefer.
2. Furnaces
Furnaces burn fuel to warm air, which is then distributed throughout your home via a system of ducts. They commonly use propane or natural gas, although some models use heating oil. Electric furnaces also exist but are generally less efficient and slower to heat. Furnaces are powerful heaters but produce toxic fumes like carbon monoxide that must be properly vented for safety.
3. Heat Pumps
Heat pumps work by transferring heat from one place to another. In winter, they move heat from the outdoors into your home, and in summer, they reverse the process to provide cooling. Heat pumps are highly efficient, using about 50% less electricity than a comparable furnace.
4. Forced Air Heating Systems
Forced air heating systems use a furnace or heat pump to warm air, which is then distributed throughout your home via ductwork. Cool air is pulled into the system through air returns, heated, and then pushed back out through vents in each room. These systems provide efficient and quick heating and can be integrated with air conditioning for year-round climate control.
Packaged Systems
Packaged HVAC systems are a type of system that combines both heating and cooling functions into a single outdoor unit. This all-in-one design saves indoor space, making them a popular choice for smaller homes or buildings with limited interior space.
While packaged systems offer the convenience of a compact, space-saving design, they are generally less powerful and efficient compared to separate heating and cooling units. This is because the single outdoor unit must handle both functions, which can lead to reduced performance and higher energy consumption.
Despite these limitations, packaged systems remain a popular choice for small homes, apartments, and commercial buildings where indoor space is at a premium. They are also relatively easy to install and maintain, as all the components are contained within a single unit.
Radiant Heating
Radiant heating is a type of HVAC system that directly heats the walls, floor, or ceiling of a room, rather than the air itself. This method of heating provides a comfortable, even warmth throughout the space, and can be more energy-efficient than forced air systems.
There are two main types of radiant heating systems: hydronic and electric. Hydronic systems use hot water or steam from a boiler to heat the surfaces of the room.
Electric radiant heating systems use a network of electric heat cables or mats installed beneath the flooring or behind the walls. These systems are typically easier to install than hydronic systems and can be a good choice for retrofit projects or smaller spaces.
One of the main advantages of radiant heating is its energy efficiency. By directly heating the surfaces of the room, radiant systems can provide a comfortable temperature at a lower thermostat setting compared to forced air systems. This can lead to significant energy savings over time.
However, radiant heating can be more difficult and expensive to install, especially in homes that were not originally designed for this type of system.
Geothermal Heating and Cooling Systems
Geothermal heating and cooling systems, also known as ground-source heat pumps, are a highly efficient and environmentally friendly type of HVAC system that utilizes the stable temperatures found deep underground to heat and cool your home.
These systems function by circulating a water or antifreeze solution through a loop of pipes buried deep underground, where temperatures remain relatively constant year-round. In the winter, the fluid absorbs heat from the ground and carries it to a heat pump inside the home, which concentrates the heat and distributes it throughout the living space.
In the summer, the process is reversed, with the heat pump extracting heat from the indoor air and transferring it to the fluid, which then carries the heat back underground.
One of the main advantages of geothermal systems is their exceptional efficiency. Because they rely on the stable temperatures found deep underground, they can provide heating and cooling much more efficiently than traditional air-source heat pumps or furnaces. This efficiency translates to significant energy savings for homeowners, as well as reduced environmental impact.
However, the main drawback of geothermal systems is their high upfront installation cost. Installing the underground loop requires extensive excavation work, which can be disruptive to landscaping and may not be feasible on all properties.
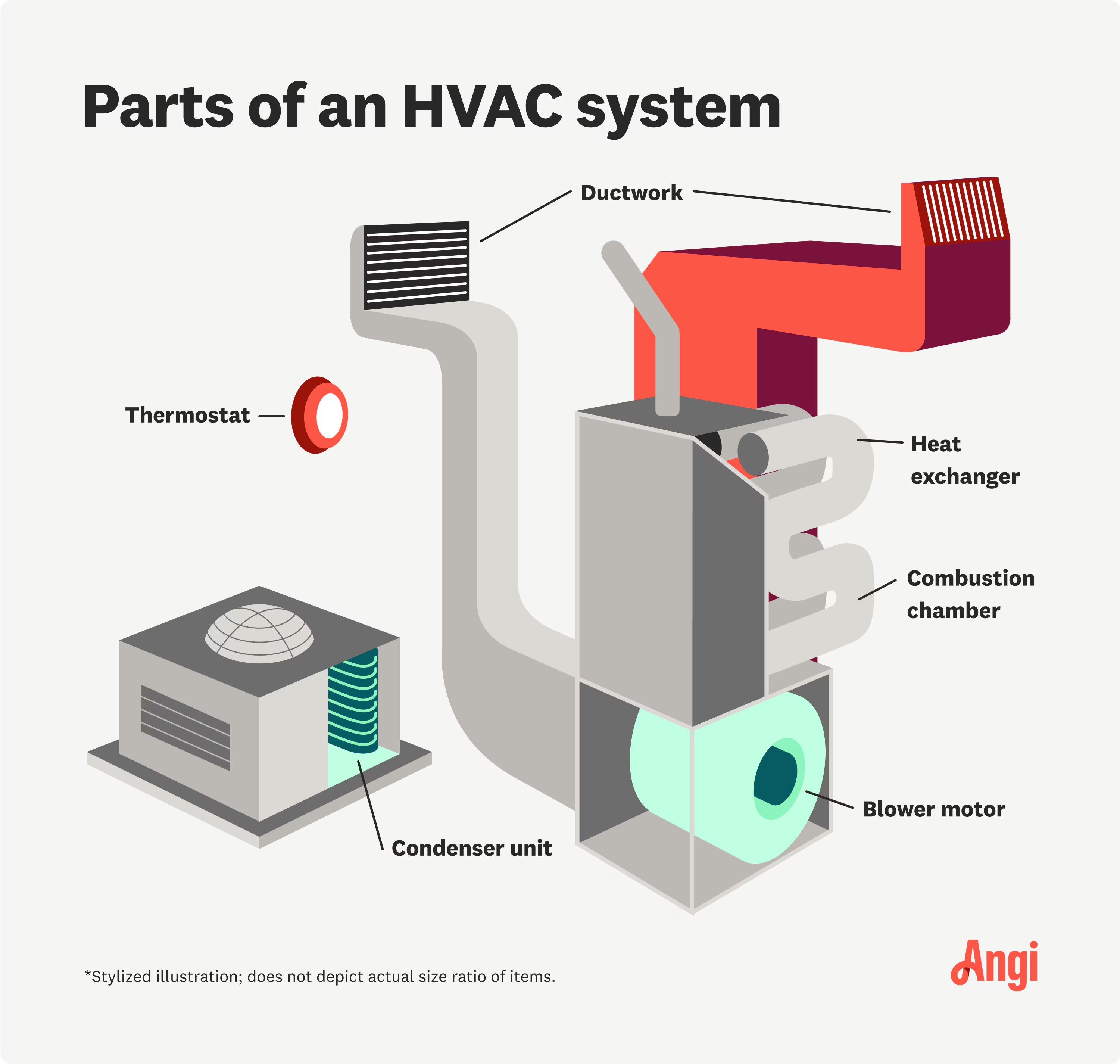
Components of HVAC Systems
Understanding the function and importance of each component can help you better maintain your system and get optimal performance.
Source: Angi
1. Ductwork
The ductwork is a network of tubes that distribute conditioned air throughout your home. It is an integral part of forced air systems, providing even heating and cooling in every room.
2. Vents and Registers
These are the openings in walls, floors, or ceilings through which warm or cool air enters the room. They can be adjusted to control airflow and direction, allowing for customized comfort.
3. Refrigerant Lines
In air conditioners and heat pumps, refrigerant lines carry refrigerant between the indoor and outdoor units. These lines are essential for the heat transfer process that enables cooling and heating.
4. Evaporator Coil
Located in the indoor unit, the evaporator coil absorbs heat from the indoor air as the refrigerant evaporates. This is a critical component of the cooling process in air conditioning systems and heat pumps.
5. Condenser Coil
Found in the outdoor unit, the condenser coil releases the absorbed heat outside as the refrigerant condenses. It works in tandem with the evaporator coil to complete the heat exchange process.
6. Compressor
The compressor is responsible for pumping and compressing refrigerant through the system, enabling the heat exchange process. It is located in the outdoor unit and is a key component for both air conditioning and heat pumps.
7. Air Handler
The air handler distributes air through the HVAC system and typically houses the evaporator coil and blower. It works with both heating and cooling systems to distribute conditioned air throughout your home.
8. Blower Motor
The blower motor powers the fan in the furnace or air handler, maintaining adequate airflow for heating and cooling operations.
9. Filters
HVAC filters trap dust, pollen, and other particles, helping to improve indoor air quality. They are essential for maintaining system efficiency and protecting components from debris.
10. Heat Exchanger
In furnaces, the heat exchanger transfers heat from the combustion process to the air being circulated. This component is critical for converting energy from fuel into usable heat.
11. Thermostat
Acting as the control system for your HVAC, the thermostat allows you to set and adjust the desired temperature. Programmable or smart thermostats can provide scheduling and remote control capabilities, enhancing energy efficiency.
According to Project Drawdown, smart thermostats can save 10–15 percent of energy needs while improving comfort and convenience.
How to Choose the Right HVAC Brand?
When evaluating different brands, consider the following factors:
1. Noise Ratings
The noise levels of both indoor and outdoor units can significantly impact your comfort, especially in bedrooms and living areas. Quieter units can enhance your indoor environment, so be sure to assess the noise ratings of different brands and models. Look for systems with well-insulated compressors and variable-speed fans, which can help reduce noise levels.
2. Sizing Accuracy
Proper sizing is essential for an HVAC system to efficiently heat and cool your home. Check that the BTU capacity of the unit matches what is advertised by the manufacturer. An accurately sized system will prevent issues related to undersizing, such as inadequate heating or cooling, or oversizing, which can lead to short-cycling and increased wear and tear on the equipment.
3. Efficiency
Compare the tested Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) rating to the manufacturer’s claims. Higher SEER ratings indicate better energy efficiency, which can result in lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact. Look for brands that consistently deliver on their efficiency promises, as this can lead to significant savings over the life of the system.
4. Reliability
Research feedback from other customers and HVAC technicians regarding the frequency of breakdowns or repairs for different brands. A reliable HVAC system will have fewer issues and a longer lifespan, saving you money on maintenance and replacement costs in the long run. Choose a brand known for producing durable, dependable equipment.
5. Warranties
Reputable HVAC companies will stand behind their products with strong warranty terms. Look for brands that offer at least 10 years of coverage on major components, such as the compressor, heat exchanger, and coils. A longer warranty indicates the manufacturer’s confidence in the durability and longevity of their equipment.
6. Cost
While the upfront cost of an HVAC system is important, it’s crucial to evaluate whether the performance and durability justify the price tag. Higher-end models may have steeper initial costs but can offer better long-term value through improved efficiency, reliability, and longevity. Consider the total cost of ownership, including energy savings and potential repair costs, when comparing different brands and models.
Importance of HVAC Systems
1. Comfort
HVAC systems help in maintaining a comfortable indoor environment by regulating temperatures, controlling humidity, and providing zoning capabilities. Humidity control prevents issues like mold growth, dry skin, and respiratory irritation by maintaining optimal moisture levels.
Zoning allows different areas to be conditioned to different temperatures, maintaining personalized comfort for occupants with varying preferences.
The ability to control humidity, provide zoning, and maintain desired temperatures highlights the importance of HVAC systems in creating comfortable living and working spaces. A well-maintained and efficient HVAC system significantly improves occupants’ quality of life, making it an essential component of modern buildings.
2. Air Quality
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), air cleaners and HVAC filters can help reduce airborne contaminants, including viruses, in a building or small space.
In addition to filtration, HVAC systems provide proper ventilation, which is essential for diluting indoor contaminants and bringing in fresh outdoor air. This helps maintain a healthy balance of oxygen and reduces the concentration of harmful particles.
Furthermore, HVAC systems can manage and reduce unpleasant odors. By filtering the air and providing adequate ventilation, these systems help eliminate odors from cooking, pets, or other sources, creating a more pleasant living or working space.
3. Energy Efficiency
HVAC systems have become increasingly energy-efficient thanks to advanced technologies like variable speed motors and smart thermostats. Variable speed motors adjust output based on heating or cooling needs, consuming only the necessary energy.
These energy-efficient technologies and strategies significantly reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, allowing HVAC systems to play an important role in mitigating the environmental impact of buildings.
As more homes and businesses adopt energy-efficient HVAC solutions, the collective reduction in carbon footprint contributes to a more sustainable future.
4. Health and Safety
HVAC systems play a vital role in maintaining health and safety in indoor environments. By controlling indoor humidity levels, HVAC systems prevent the growth of mold and mildew, which can cause respiratory issues and other health problems.
Regular maintenance of fuel-burning heating systems, helps in reducing the risk of carbon monoxide (CO) leaks. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), CO poisoning causes an average of 420 deaths per year in the United States.
By addressing indoor air quality, allergens, and potential safety hazards, HVAC systems contribute significantly to creating a healthy and safe living or working environment.
5. Consistent Air Circulation
HVAC systems are essential for maintaining consistent air circulation in indoor environments, which is vital for the health, comfort, and safety of occupants. By continuously circulating air, HVAC systems help prevent the buildup of indoor pollutants, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and carbon dioxide, which can have negative health effects.
Adequate air circulation also provides a consistent supply of oxygen throughout the building. This is particularly important in densely occupied spaces, where oxygen levels can quickly become depleted without proper circulation.
Furthermore, HVAC systems help maintain balanced air pressure within the building. This prevents issues such as drafts, uneven temperatures, and air infiltration from the outdoors. By regulating air pressure, HVAC systems enhance overall comfort and contribute to a more stable and secure indoor environment.
6. Environmental Impact
HVAC systems have a significant role in promoting sustainable living and supporting global efforts to combat climate change. By incorporating energy-efficient technologies and strategies, modern HVAC systems can significantly reduce energy consumption in buildings. This not only lowers utility costs for occupants but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with energy production and consumption.
Energy-efficient HVAC operations contribute to the global fight against climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. As buildings account for a significant portion of global energy consumption, optimizing HVAC efficiency can have a substantial impact on mitigating climate change.
How to Choose an HVAC Company for Installation and Maintenance
Consider the following factors when choosing an HVAC company:
1. Reputation and Recommendations
Word-of-mouth recommendations from friends, family, and neighbors can provide valuable insights into a company’s quality of service. Check online reviews on platforms like Google, Yelp, and Better Business Bureau to gauge customer satisfaction and overall company reputation.
2. Licensing and Certification
Verify that the HVAC company is licensed, insured, and certified by reputable industry organizations such as North American Technician Excellence (NATE). These certifications demonstrate a commitment to professionalism, ongoing education, and adherence to industry best practices.
3. Experience and Expertise
Choose a company with several years of experience and expertise in installing and servicing your specific type of HVAC system, whether it’s a central air conditioner, heat pump, ductless mini-split, or geothermal system. Experienced technicians are better equipped to diagnose and solve complex issues, recommend appropriate solutions, and optimize your system’s performance.
4. Local Climate Considerations
Select an HVAC company that is well-versed in the unique climate challenges of your area. A company with local experience will be better equipped to recommend systems and solutions tailored to your region’s specific weather conditions, such as high humidity, extreme temperatures, or coastal environments.
5. Customer Service and Communication
Evaluate the company’s customer service, responsiveness, and communication during your initial interactions. A reputable HVAC company should be prompt in responding to your inquiries, transparent about their services and pricing, and willing to answer your questions thoroughly.
They should also provide clear, written estimates and contracts outlining the scope of work, timeline, and payment terms. Good communication and customer service are essential for a smooth installation process and ongoing maintenance support.
Contact HVAC Angel For All Your HVAC Needs
At HVAC Angel, we are committed to providing top-notch HVAC services so that your home or business remains comfortable and energy-efficient. With our team of highly skilled and certified technicians, state-of-the-art equipment, and years of experience in the industry, we are the best choice for all your HVAC needs.
We understand that when your HVAC system isn’t working properly, despite your best efforts to maintain it, you need professional help. That’s where we come in. Our technicians use the latest diagnostic tools and techniques to quickly identify and resolve any issues with your system, whether it’s a simple repair or a complex installation.
We have the knowledge and expertise to handle any challenge that comes our way. From basic maintenance to complete system overhauls, we’ve seen it all and know how to get the job done right.
Don’t let HVAC problems disrupt your comfort or productivity. Contact HVAC Angel today and experience the difference that professional, reliable HVAC service can make. We’re here to help you stay comfortable all year round.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is HVAC AC gas or electric?
HVAC systems can be powered by either gas or electricity, depending on the specific components. For example, furnaces often run on natural gas or propane, while air conditioners and heat pumps typically use electricity.
2. Is HVAC AC or DC?
HVAC systems use alternating current (AC) for power supply, as it is the standard form of electricity provided by utility companies. However, some components within the system, such as certain motors or controls, may use direct current (DC).
3. How often should HVAC systems be maintained?
HVAC systems should be professionally maintained at least once a year, typically before the start of the heating or cooling season. However, regular filter replacements and basic cleaning can be done by homeowners every 1-3 months.
4. Are there government incentives for upgrading to energy-efficient HVAC systems?
Yes, there are often government incentives, such as tax credits or rebates, available for upgrading to energy-efficient HVAC systems. These incentives vary by location and may be offered by federal, state, or local governments, as well as utility companies.
5. Can I install an HVAC system myself, or should I hire a professional?
It is strongly recommended to hire a professional HVAC technician for installation, as it requires specialized knowledge, tools, and adherence to local building codes and safety regulations. Attempting a DIY installation can void warranties, compromise system efficiency, and potentially create safety hazards.


![9 Reasons That Causes an AC Unit to Freeze Up: [Troubleshooting Guide]](https://hvacangel.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/what-causes-a-ac-unit-to-freeze-up-1024x683.png)